Introduction
Professionals in law make up judges. How to become an Indian judge is a question nearly all applicants have. Within the Indian civil service, judges are regarded as highly esteemed members. What a judge does, who they are, and how to become one in India will all be covered in this article. Honor and respect are inherent in the role of the judge. Both the prosecutors and the defendants are listened to by the judge, who also supervises the court proceedings. Having heard from all sides and considering the relevant legal precedents, he or she renders a judgment in the courtroom.
Understanding the Role of a High Court Judge
Constitutional interpretation authority is granted to the state’s highest court of appeals, the High Court. It is responsible for defending citizens’ fundamental rights. It also performs consulting and supervising duties. However specific provisions for the authority and jurisdiction of a high court are absent from the Constitution.
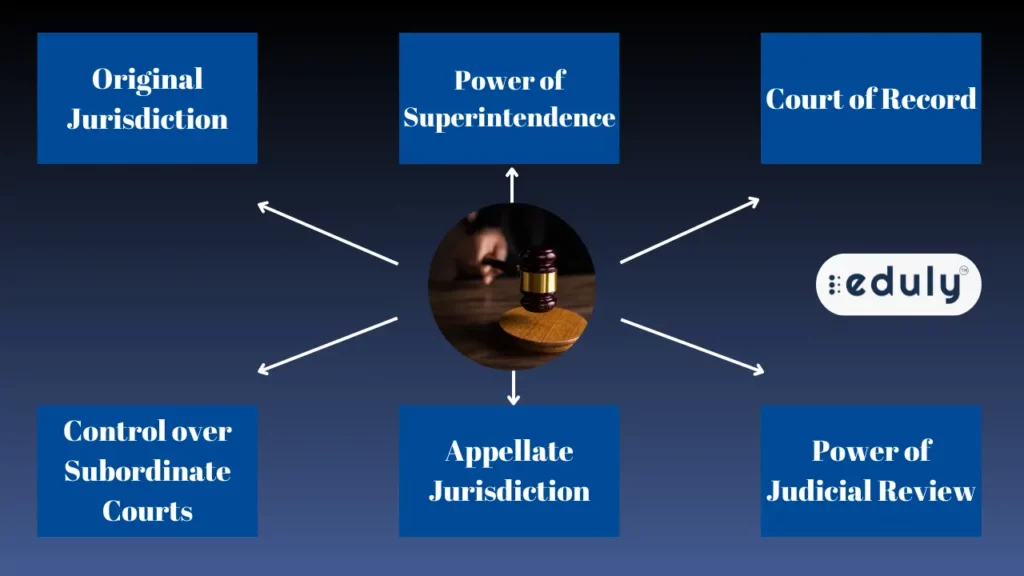
The High Court’s jurisdiction is listed below:
Original Jurisdiction
Under these circumstances, the petitioner need not file an appeal and may proceed straight to the High Court. The State Legislative Assembly, weddings, the upholding of fundamental rights, and the transfer of cases from other courts are the main areas in which it applies.
Power of Superintendence
No other lower court has the unique authority to superintend; the High Court alone possesses it. This gives the High Court the authority to make regulations for how its lower offices and courts must keep records, to settle disputes over fees given to sheriff officers, clerks, and attorneys, and to establish procedures for holding court cases.
Court of Record
For the sake of perpetuity, it entails recording high court rulings, actions, and procedures. In no court can these records be further examined. For disdaining itself, it can chastise.
Control over Subordinate Courts
The supervisory and appellate jurisdictions are being expanded by this. If a matter concerns a significant legal issue, it stipulates that the High Court may withdraw it from consideration in any lower court. Both self-resolving and remanding the matter to the same court are options for handling legal disputes.
Appellate Jurisdiction
This is for instances in which someone has filed a complaint regarding a review of a decision made by the territorial district court or lower court. Two further classifications for this power are as follows:
- Civil Jurisdiction: District court, civil district court, and subordinate court decisions and judgments are included in this.
- Criminal Jurisdiction: The sessions court and other sessions courts’ rulings and orders are included in this.
Power of Judicial Review
Examining whether legislative and executive orders from the federal and state governments are constitutional is one of the High Court’s numerous powers. Although our constitution does not use the term “judicial review,” the High Court is expressly granted this authority by Articles 13 and 226.
Eligibility Criteria
For an individual to be appointed as a judge in any Indian High court, they must meet specific eligibility requirements. The set of qualifying requirements needed to appoint judges to the High Court are listed below:
- A minimum of five years of experience as a barrister should have been required.
- Serves the Zila court for a minimum of three years and has over ten years of experience as a civil servant.
- A defendant in any High Court who has been a leader for more than ten years.
- The maximum age for a judge to be is 62.
While it is needed by law for each state to have its own High Court, specific states continue to lack one. Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, Tripura, Meghalaya, and Arunachal Pradesh are the seven states with combined High Courts.
The Pathway to Becoming a High Court Judge
It’s possible to start looking for judicial chances after practicing law for a minimum of two years. Since many federal judges hold lifetime appointments, which limits the number of open seats, becoming a judge is a competitive endeavor. An individual can become a judge in one of three ways:
- Election: Many times, local judges run for office and win. States have different election laws, and some of the differences are the number of terms a judge may serve the timing of elections, and term lengths.
- Temporary Appointment: Some states permit the appointment of a government appointee to replace an elected judge who is removed from the bench or decides to stand down in midterm. The appointed judge will typically hold these seats until the next regular election, but if that election is too far off, a special election may be called instead.
- Appointed: Executives, including governors and the president, appoint many judges. appointments are frequently lifelong positions for federal positions. Appearing on a shortlist that is forwarded to the person in charge of scheduling the appointment is typically the first step in the process. After being selected for the position based on a screening process, shortlisted candidates typically appear for confirmation hearings before a state or federal legislative body.
The Selection Process
Following discussions with the Chief Justice of India and the Governor of the relevant State, the Chief Justice of a High Court is appointed. In parallel, a collegium made up of the CJI and the two seniormost judges provides consultations for other High Court justices. What needs to happen is this procedure:
- The concerned High Court Chief Justice, after consulting with the two most senior judges, makes the initial move.
- Sending the suggestion to the Union Law Minister is the Governor’s advice after it has been forwarded to the Chief Minister.
According to the procedures followed by Chief Justices from outside their states, The selection process takes place for the High Court Chief Justice. All of the state governors are consulted if it is for a joint High Court.
Qualities of a Successful High Court Judge
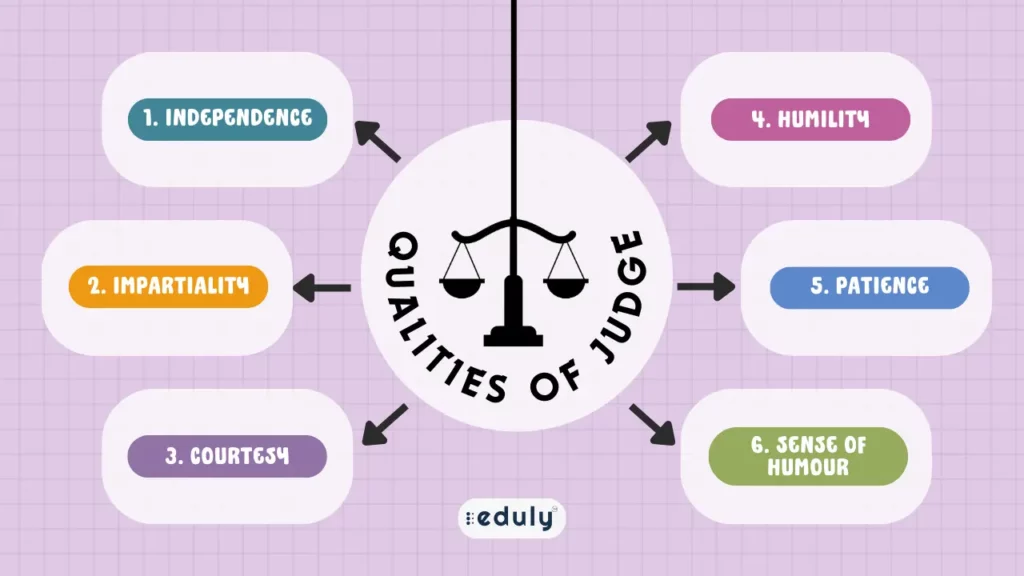
1. Independence
Independent thought is the first attribute of a competent judge that I will consider. Here, “independence” means that a judge is free from any commitments, duties, or conflicts of interest that can improperly influence the performance of their official duties.
2. Impartiality
Impertinence is closely related to impartiality, the second attribute. It is impartiality, as stated in the oath of office, that forms the foundation of the judicial role. Individuals must be treated equally regardless of their status when they appear in court—rich and powerful or poor and marginalized.
3. Communication Skills
For a judge to succeed in their work, effective communication skills are essential, even though they might not be characteristics in the traditional sense. A jury’s instructions and choices must be made by judges during a trial. For people who have to go by the regulations and directions, they must do this in an easy-to-understand manner.
4. Courtesy
In addition to being an essential human quality, courtroom etiquette is also a critical competency. Courtesy hasn’t always been associated with civility. In the past, some judges thought that the office’s aura and authority were enhanced by their cold, unyielding demeanor. Those days are gone. Everyone who shows up in court has a right to be treated with decency and consideration. Those with mental problems, self-defense attorneys, and defendants accused of heinous crimes are all included in this.
5. Humility
Humility can be advantageous to the legal system. It is appropriate to acknowledge, either during the trial or after it is over when judges get legal support. Similarly, it is appropriate to acknowledge one’s error and thank the party that explained it when a judge misunderstands the facts of a case.
6. Sense of Perspective
This quality is called perspective perception. This is the ability to set priorities for your time and effort based on what is and is not worth thinking about. When managing a difficult case, judges particularly need to have a sense of perspective. Numerous elements, such as the volume or complexity of the evidence and submissions, and bad behavior by a party, witness, or even legal expert, can make a trial difficult.
7. Patience
It is a widely held belief that patience is a virtue. For judges as well, it is an essential attribute. Judges need to be patient, especially when hearing dubious submissions or unconvincing evidence. The rules of natural justice require that the parties be allowed to present their case fairly before a decision is made. A judge who acts rashly by voicing firm conclusions before they are completely formed or by cutting off a party before their case is concluded may be ordered to retry the case by an appeals court.
8. Sense of Humour
A major undertaking with hefty responsibilities and liabilities is justice administration. It is inappropriate for judges to attempt stand-up comedy in the courtroom since court users are under a lot of stress during court hearings. It does not follow, however, that judges have to be tense and melancholy all the time.
Career Progression and Opportunities
The titles of Chief Justice of India, Justice of the Supreme Court, Chief Justice of High Courts, and Judge of High Courts are the only positions in a judge’s career hierarchy; there are no senior and junior levels. They have their wages listed below.
| Designation | Salary |
| Chief Justice of India | Rs. 2,80,000/- p.m |
| Judges of the Supreme Court | Rs. 2,50,000/- p.m. |
| Chief Justice of the High Court | Rs. 2,50,000/- p.m. |
Conclusion
A uniform method for addressing social issues is found in the Indian legal system. An Indian judicial career offers the younger generation a plethora of opportunities to integrate into the system and effectively serve the country. In India, the pay for judges varies according to their particular category. The Indian judiciary holds this position as its most significant one. Youths are responsible for putting the law into practice, interpreting it, and applying its requirements. A significant amount of effort, commitment, and resolve towards the legal system are required.




